The term pharmacovigilance defines programs – often public and of public importance – for the control and surveillance of marketed drugs. It is generally the national and international health authorities’ responsability. Pharmacovigilance is born from the need to increase the control of efficacy of drugs at the time of their use on a large scale after they are placed on the market.
The term pharmacovigilance defines programs – often public and of public importance – for the control and surveillance of marketed drugs. It is generally the national and international health authorities’ responsability. Pharmacovigilance is born from the need to increase the control of efficacy of drugs at the time of their use on a large scale after they are placed on the market.
The previous clinical experimental phases, in fact, are used on selected groups of patients, in optimal conditions, and then, in the moment in which the new medicinal product is used by the general population, it could happen some side effects not found in the experimental stage. The pharmacovigilance can be considered, therefore, a permanent monitoring system, and properly it constitutes Phase IV of pharmaceutical testing (post-marketing).
The haemovigilance (supervision of blood) is the ensemble of all the procedures adopted by the national network of transfusion personnel to supervise unexpected adverse reactions and serious accidents that may occur in the transfusion process; it also includes the epidemiological surveillance of infectious diseases transfusion transmitted, which is, in fact, a prerequisite for infectious disease surveillance of donated blood. It is, in fact, collected information on infectious markers (HIV, HBV, HCV, Treponema pallidum) of each unit of blood collected.
27 June 2024
The underevaluated impacts of the therapeutic revolution of hemophilia on women and girls
The advent of new treatment options over the last decades has markedly improved the lives of male persons with hemophilia (PwH). However, this therapeutic revolution has not benefited women and girls with hemophilia (WGH) and symptomatic carriers of the disease to the same extent as their male counterparts. This inequity is primarily due to the […]
30 May 2022
Intracranial Haemorrhage in Haemophilia Patients Is Still an Open Issue: The Final Results of the Italian EMO.REC Registry
Abstract: Background: Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) is a highly serious event in patients with haemophilia (PWH) which leads to disability and in some cases to death. ICH occurs among all ages but is particularly frequent in newborns. Aim: The primary aim was to assess the incidence and mortality due to ICH in an Italian population of […]
21 March 2022
Chikungunya and Mayaro infective viruses in components of blood
Detection and analysis of blood donors seropositive for syphilis Background:The increasing incidence of syphilis worldwide has called attention to the risk of transmission by transfusion. Aims:To determine the prevalence of active syphilis in blood donors and characterise the serological profile of syphilis-positive donors. Methods: Samples positive for Treponema pallidum using the chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) during […]
23 March 2021
The SISET (Italian Society of Internal Medicine provides some practical information for patients with thrombosis and serious bleeding diseases in case of COVID-19 vaccination
Patients on oral anticoagulant treatment and patients with severe bleeding diseases People being treated with anticoagulant therapy and patients with bleeding disorders have a generic contraindication to intramuscular injections due to the risk of hematoma. However, anticoagulant therapy is in most cases indicated for diseases that increase the risk of contracting the COVID-19 […]
17 March 2021
ISTH STATEMENT ON ASTRAZENECA COVID-19 VACCINE AND THROMBOSIS
The International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) recommends that all eligible adults continue to receive their COVID-19 vaccinations, despite the recent decisions by Austria, Denmark, Norway and Iceland to at least temporarily suspend the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine due to reports of thrombosis. At this time, the small number of reported thrombotic events relative […]
15 March 2021
Risk for Hepatitis E Virus Transmission by Solvent/Detergent–Treated Plasma
Hepatitis E has emerged as a major transfusion-transmitted infectious risk. Two recipients of plasma from 2 lots (A and B) of pooled solvent/detergent-treated plasma were found to be infected by hepatitis E virus (HEV) that was determined to have been transmitted by the solvent/detergent-treated plasma. HEV RNA viral loads were 433 IU in lot A […]
25 January 2021
Detection and analysis of blood donors seropositive for syphilis
Background:The increasing incidence of syphilis worldwide has called attention to the risk of transmission by transfusion. Aims:To determine the prevalence of active syphilis in blood donors and characterise the serological profile of syphilis-positive donors. Methods: Samples positive for Treponema pallidum using the chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) during blood donor screening from 2017 to 2018 were tested by […]
25 November 2020
Risk for Hepatitis E Virus Transmission by Solvent/Detergent–Treated Plasma
Hepatitis E has emerged as a major transfusion-transmitted infectious risk. Two recipients of plasma from 2 lots (A and B) of pooled solvent/detergent-treated plasma were found to be infected by hepatitis E virus (HEV) that was determined to have been transmitted by the solvent/detergent-treated plasma. HEV RNA viral loads were 433 IU in lot A […]
12 June 2020
Screening Blood Donors for HIV, HCV, and HBV at the American Red Cross: 10-Year Trends in Prevalence, Incidence, and Residual Risk, 2007 to 2016
Prevalence, incidence and residual risk of HIV, HCV and HBV are critical indicators of the safety of the blood supply. The American Red Cross routinely monitors these markers. Herein the results of testing over 58 million donations from 2007 to 2016 are reported. The prevalence and incidence of these infections has declined or remained essentially […]
12 March 2020
INACTIVATION OF THREE EMERGING VIRUSES – SEVERE ACUTE RESPIRATORY SYNDROME CORONAVIRUS, CRIMEAN-CONGO HAEMORRHAGIC FEVER VIRUS AND NIPAH VIRUS – IN PLATELET CONCENTRATES BY ULTRAVIOLET C LIGHT AND IN PLASMA BY METHYLENE BLUE PLUS VISIBLE LIGHT
Emerging viruses like severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) and Nipah virus (NiV) have been identified to pose a potential threat to transfusion safety. In this study, the ability of the THERAFLEX UV-Platelets and THERAFLEX MB-Plasma pathogen inactivation systems to inactivate these viruses in platelet concentrates and plasma, respectively, was […]
11 March 2020
Coronavirus Disease 2019: Coronaviruses and Blood Safety
With the outbreak of unknown pneumonia in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, a new coronavirus, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), aroused the attention of the entire world. The current outbreak of infections with SARS-CoV-2 is termed Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). The World Health Organization declared COVID-19 in China as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. Two other coronavirus infections-SARS […]
17 February 2020
Current state of play regarding dental extractions in patients with haemophilia: Consensus or evidence‐based practice? A review of the literature
Tooth extractions are quite common surgical procedures in patients with haemophilia, in particular in older age or in countries with restricted resources. Uptodate, the optimal management of replacement therapy (RT, dosage and duration of treatment) are scant and only low levels of evidence are available. A recent article has reviewed the haematological treatment protocols and […]
16 February 2020
A retrospective Analysis of the Use of 3-Factor Prothrombin Complex Concentrates for Refractory Bleeding After Cardiopulmonary Bypass in Children Undergoing Heart Surgery: A Matched Case-Control Study
The 3-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (3FPCC) may be used off-label to treat refractory bleeding during cardiac surgery in children. This retrospective study examined the rate of clinical complications following the use of 3FPCC. Patients treated with 3FPCC were matched to controls for age, gender, prematurity, weight, cardiopulmonary bypass times, and cross-clamp times. Fifty-nine cases were […]
15 February 2020
Early administration of fibrinogen concentrate is associated with improved survival among severe trauma patients: a single-centre propensity score-matched analysis
Low fibrinogen levels after severe trauma are associated with haemostatic impairment, massive bleeding, and poor outcomes. Fibrinogen supplementation is able to improve haemostatic function, the early administration of fibrinogen concentrate (FC) has here been associated with improved survival in severe trauma patients.A single-centre retrospective study evaluated patients with severe trauma. The exclusion criteria included age […]
21 January 2020
Prevalence, incidence and residual risk of transfusion-transmitted hepatitis B virus infection in Italy from 2009 to 2018
In Italy, nucleic acid testing for hepatitis B virus (HBV) in donor screening allows the detection of infections in the window phase or occult infections allowing to avoid potential transmissions. Epidemiological data on HBV infection in blood donors have here been evaluated, the residual risk of HBV transmission has also been studied over a 10-year […]
19 January 2020
The growing importance of achieving national self-sufficiency in immunoglobulin in Italy. The emergence of a national imperative
The current plasma collection capacity of several countries will be soon unable to afford the growing need of immunoglobulin (IG) therapies. United States (US) of America, are currently generating two thirds of the worldwide supply of plasma for fractionation. Reduced availability of IG occur whenever the demand for the product outstrips the supply. Currently the […]
17 January 2020
Decreases in U.S. Blood Donors even if Eligible Donors are increasing in the last ten years
Red Blood Cells (RBC) and whole blood cell transfusions have been reported to decrease by approximately 10% in the last ten years, there has been a greater decline in the units of blood collected, thus availability of blood products is at risk. An epidemiologic study has evaluated eligible donors in US, based on donor exclusion […]
15 January 2020
Mechanisms and potential implications of ineffective platelets transfusion
Platelet transfusions may be ineffective for bleeding prevention in subjects with inherited platelet disorders (i.e. Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia, Bernard-Soulier syndrome) or in acquired conditions like dual antiplatelet therapy and acquired platelet function disorders. In a recently published research, with the aim to investigate why platelet transfusions have variable effectiveness, researchers assessed mice with defects in each […]
19 December 2019
Uncovering occult hepatitis B in blood donations: a tale of two worlds
For almost fifty years, improvements in donor selection and screening have led to a continuous reduction in the risk of transfusion-transmitted hepatitis B virus (HBV). However, transmission can still occur when blood is collected from hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) negative donors during the pre-seroconversion window period. Another source of transmission is represented by donors […]
16 December 2019
Prevalence, incidence and residual risk of transfusion-transmitted hepatitis B virus infection in Italy from 2009 to 2018
In Italy, the use of nucleic acid testing for hepatitis B virus (HBV) in donor screening has allowed the detection of infections in the window phase, as well as the presence of occult infections which could potentially be transmitted. The aim of this study was to analyse the trends of epidemiological data focused on HBV […]
20 November 2019
Buffy coat-derived platelets cryopreserved using a new method: results from a pivotal clinical trial on thrombocytopenic patients with acute leukaemia
The administration of cryopreserved platelets (PLTs) may overcome the limits of platelet shortage and availability, especially during some seasons or in specific contexts like rural areas. After in vitro validation studies, ad hoc prepared buffy coat-derived pooled platelet concentrates (BC-PLTs), treated with dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) and cryopreserved (CRY BC-PLTs) at -80°C with a modified Valeri […]
17 September 2019
New Hemostatic Agents: Perioperative Anesthetic Considerations
AIM: Pharmacologic agents with procoagulant effects and antidotes against antithrombotic drugs play an important role in the prevention and management of perioperative coagulopathic bleeding. Aim of this narrative review is knowledge transfer on new and renewed hemostatic agents to anesthesiologists and other physicians involved in perioperative medicine. METHODS: The literature search was performed in PubMed […]
16 May 2019
Risk factors for postoperative complications of orthopedic surgery in patients with hemophilia: Second report
This study was conducted to investigate the incidence in patients with hemophilia of postoperative complications and risk factors for these complications. Overall, 12 (6.5%) patients developed a postoperative infection. There were 6 (3.4%) postoperative surgical site infections. The presence of an inhibitor was the only risk factor for surgical site infection. Risk factors for delayed […]
23 February 2019
Parvovirus B19: What Is the Relevance in Transfusion Medicine?
Parvovirus B19 (B19V) has been discovered in 1975. The association with a disease was unclear in the first time after the discovery of B19V, but meanwhile, the usually droplet transmitted B19V is known as the infectious agent of the “fifth disease,” a rather harmless children’s illness. Due to the infection path via droplet transmission, many […]
21 February 2019
Viral metagenomics and blood safety
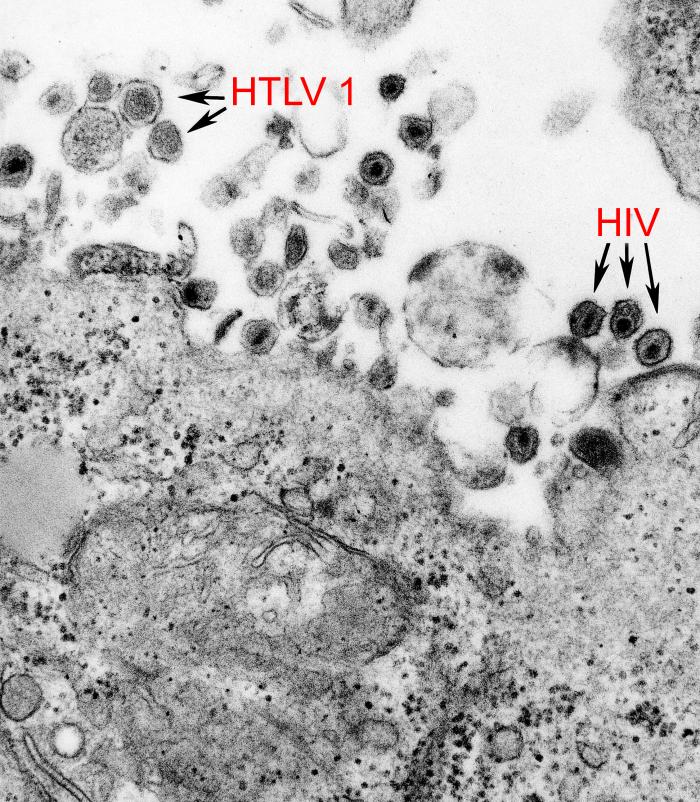
The characterization of the human blood-associated viral community (also called blood virome) is essential for epidemiological surveillance and to anticipate new potential threats for blood transfusion safety. Currently, the risk of blood-borne agent transmission of well-known viruses (HBV, HCV, HIV and HTLV) can be considered as under control in high-resource countries. However, other viruses unknown […]
19 February 2019
Haematology patients and the risk of transfusion transmitted infection
A 2014 study by NHS Blood and Transplant indicated that over one quarter of red cells were transfused to patients with haematological conditions. For platelet components, the figure is higher. Certain diagnostic groups, such as haemoglobinopathies, myelodysplastic syndromes and some haemato-oncology patients, receive multiple transfusion episodes, either over long periods, or more intensively over shorter […]
17 February 2019
Prophylactic treatment of bleeding episodes in children <12 years with moderate to severe hereditary factor X deficiency (FXD): Efficacy and safety of a high-purity plasma-derived factor X (pdFX) concentrate
Hereditary factor X (FX) deficiency (FXD) is a rare autosomal recessive bleeding disorder with an estimated prevalence of 1:500 000-1:1 000 000. The bleeding patterns of FXD are broadly similar to those seen in haemophilia A and B: spontaneous joint and muscle bleeds are common, as are mucocutaneous bleeding (eg, nose, oral cavity and gastrointestinal […]
15 February 2019
False positive viral marker results in blood donors and their unintended consequences
Universal donor screening for the major transfusion relevant viruses, hepatitis B virus (HBV), human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 (HIV-1/2) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) has contributed to the current very low risk of transmitting infectious diseases by transfusion. While contemporary blood donor screening assays have excellent specificity, defined as the probability of giving […]
13 February 2019
Pathogenic immune response to therapeutic factor VIII: exacerbated response or failed induction of tolerance?
Therapeutic factor VIII is highly immunogenic. Despite intensive research in the last decades, the reasons why 5-30% of patients with hemophilia A (of all severities) develop inhibitory anti-factor VIII antibodies (inhibitors) following replacement therapy remain an enigma. Under physiological conditions, endogenous factor VIII is recognized by the immune system. Likewise, numerous observations indicate that, in […]
6 February 2019
Hepatitis C infection in patients with hereditary bleeding disorders: epidemiology, natural history, and management
Abstract Hereditary bleeding disorders include a group of diseases with abnormalities of coagulation. Prior to 1990, infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) was mainly transmitted via pooled plasma products as a treatment for hereditary bleeding disorders. Anti-HCV positivity in these patients may be as high as >70% in some areas, while some of them have […]
13 January 2019
Efficacy and safety of the use of platelet-rich plasma to manage venous ulcers
Venous ulcers affect 0.6%e3% of the population aged over 60; this increases up to 5% in those aged over 80. Between 70% and 80% of all ulcers that affect the legs are of venous aetiology and almost one-third turn chronic. When the underlying pathology is not managed, it is estimated that approximately 45% of individuals […]
8 January 2019
Pathogen-inactivated blood products for pediatric patients: blood safety, patient safety, or both?
The past decades have witnessed a dramatic improvement in blood product safety due to a multifaceted approach including blood donor screening, sensitive infectious disease testing, and good manufacturing practice. Current residual risks of viral transmission range from one per 1 million to one per 2 million units transfused. Pathogen reduction (PR), also called pathogen inactivation […]
10 December 2018
Hepatitis C infection in patients with hereditary bleeding disorders: epidemiology, natural history, and management
Hereditary bleeding disorders include a group of diseases with abnormalities of coagulation. Prior to 1990, infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) was mainly transmitted via pooled plasma products as a treatment for hereditary bleeding disorders. Anti-HCV positivity in these patients may be as high as >70% in some areas, while some of them have also […]
8 December 2018
Haematology patients and the risk of transfusion transmitted infection
A 2014 study by NHS Blood and Transplant indicated that over one quarter of red cells were transfused to patients with haematological conditions. For platelet components, the figure is higher. Certain diagnostic groups, such as haemoglobinopathies, myelodysplastic syndromes and some haemato-oncology patients, receive multiple transfusion episodes, either over long periods, or more intensively over shorter […]
6 December 2018
Special considerations for the use of pathogen reduced blood components in pediatric patients: An overview
Pediatric patients requiring transfusion constitute one of the most challenging areas of transfusion practice. Due to the limitations posed by their particular physiological conditions they routinely require specialized component support and more personalised transfusion care than what is routinely utilized in the care of adult patients. Pediatric patients, unlike many adult patients requiring transfusion support, […]
4 December 2018
Safety of blood, blood derivatives, and plasma-derived products
There has been concern for several decades around the possibility that prion diseases may be transmissible by blood components and / or plasma products. Whilst the evidence in respect of transmission of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is largely circumstantial, the identification of variant CJD gave rise to increased concern due to the evidence of prion […]
4 September 2018
Early start of the West Nile fever transmission season 2018 in Europe
In Europe, surveillance indicates that the 2018 West Nile fever transmission season started earlier than in previous years and with a steeper increase of locally-acquired human infections. Between 2014 and 2017, European Union/European Economic Area (EU/EEA) and EU enlargement countries notified five to 25 cases in weeks 25 to 31 compared with 168 cases in […]
26 July 2018
A nationwide retrospective study on prevalence of hepatitis E virus infection in Italian blood donors
Abstract BACKGROUND: In Europe, hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection is mainly a food-borne zoonosis, but it can also be transmitted by blood transfusion. It is usually a mild and self-limited infection. However, immunocompromised persons, who are also those more likely to undergo blood transfusions, may develop chronic hepatitis and often cirrhosis. Since this is a […]
22 May 2018
Transmission of rheumatoid arthritis through blood transfusion: a retrospective cohort study
The long preclinical phase of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), where some factors involved in RA pathogenesis circulate peripherally, raises concern of RA transmissibility through blood transfusion. Specifically, this possibility is suggested by murine RA models in which anticitrullinated peptide/protein antibodies may induce and enhance arthritis, and precursors of the RA-fibroblast-like synoviocyte cells may aggravate and spread […]
2 March 2018
Pathogen reduction/inactivation of products for the treatment of bleeding disorders: what are the processes and what should we say to patients?
Patients with blood disorders (including leukemia, platelet function disorders and coagulation factor deficiencies) or acute bleeding receive blood-derived products, such as red blood cells, platelet concentrates and plasma-derived products. Although the risk of pathogen contamination of blood products has fallen considerably over the past three decades, contamination is still a topic of concern. In order […]
28 February 2018
Haematology patients and the risk of transfusion transmitted infection
A 2014 study by NHS Blood and Transplant indicated that over one quarter of red cells were transfused to patients with haematological conditions. For platelet components, the figure is higher. Certain diagnostic groups, such as haemoglobinopathies, myelodysplastic syndromes and some haemato-oncology patients, receive multiple transfusion episodes, either over long periods, or more intensively over shorter […]
26 February 2018
Parvovirus B19: What Is the Relevance in Transfusion Medicine?
Parvovirus B19 (B19V) has been discovered in 1975. The association with a disease was unclear in the first time after the discovery of B19V, but meanwhile, the usually droplet transmitted B19V is known as the infectious agent of the “fifth disease,” a rather harmless children’s illness. But B19V infects erythrocyte progenitor cells and thus, acute […]
21 February 2018
Transfusion-Transmitted Hepatitis E: NAT Screening of Blood Donations and Infectious Dose
The risk and importance of transfusion-transmitted hepatitis E virus (TT-HEV) infections by contaminated blood products is currently a controversial discussed topic in transfusion medicine. The infectious dose, in particular, remains an unknown quantity. In the present study, we illuminate and review this aspect seen from the viewpoint of a blood donation service with more than […]
24 January 2018
Cost projections for implementation of safety interventions to prevent transfusion-transmitted zika virus infection in the United States
In August 2016, the Food and Drug Administration advised US blood centers to screen all whole blood and apheresis donations for Zika virus (ZIKV) with an individual-donor nucleic acid test (ID-NAT) or to use approved pathogen reduction technology (PRT). The cost of implementing this guidance nationally has not been assessed. Scenarios were constructed to characterize […]
22 January 2018
HEV and transfusion risk
HEV infections are mainly food- and water-borne but transfusion-transmission has occurred in both developing and developed countries. The infection is usually asymptomatic but it can lead to fulminant hepatitis in patients with underlying liver disease and pregnant women living in developing countries. It also causes chronic hepatitis E, with progressive fibrosis and cirrhosis, in approximately […]
20 January 2018
Occult hepatitis B infection and transmission risk through blood transfusion
Over the last decades, the advances in serology and viral nucleic acid testing (NAT) have significantly reduced the risk of transfusion-transmitted hepatitis B virus (HBV). The combination of HBsAg testing and NAT efficiently prevents the majority of HBV transmission. However, a specific residual risk remains associated with extremely low viral DNA levels in blood donors […]
16 January 2018
A mathematical model for estimating residual transmission risk of occult hepatitis B virus infection with different blood safety scenarios
Because anti-hepatitis B core antibody testing is not obligatory, blood donors with occult hepatitis B infection (OBI) may transmit hepatitis B virus (HBV) to a recipient despite the use of nucleic acid amplification technology (NAT) or pathogen inactivation (PI).
3 January 2018
The current state of adverse event reporting in hemophilia
Replacement of the missing clotting factor is the mainstay of hemophilia treatment. Whilst historically many hemophilia patients were infected with blood-borne viruses transmitted via plasma-derived products, nowadays the formation of alloantibodies against the missing clotting factor is the main adverse event of treatment. Areas covered: This paper provides an overview of the current national and […]
28 November 2017
Effective inactivation of a wide range of viruses by pasteurization
Virus validation guidelines were ultimately developed and issued by the European authorities, requiring manufacturers to carry out studies to demonstrate the capacity, reliability, and effectiveness of the manufacturing processes to inactivate and/or remove viruses potentially present in the starting material (plasma pool for fractionation). These guidelines required a systematic evaluation of the virus reduction potential […]
20 November 2017
Occult hepatitis B infection and transfusion-transmission risk
Despite the availability of a vaccine and the continuous development of antiviral treatments, persistent hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains a global major public health issue.It is estimated that more than two billion people worldwide have been in contact with the virus at some time in their lives and 257 million of them remain chronically […]
7 November 2017
Is there a relationship between Alzheimer disease and blood transfusion?
A recent study published in Molecular Psychiatry has shown for the first time that amyloid-β protein (Aβ), which plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease (AD), can be transmitted from animal to animal through the blood (in a model of parabiosis between transgenic AD mice and their wild-type littermates) and accumulates in […]
27 October 2017
Association between transfusion and mortality
An important study on mortality in patients recipients of red blood cell transfusion has recently been published in the international journal JAMA. This research, conducted in the Netherlands on 31,118 patients transfused with 59,320 blood units, showed an increased mortality in males receiving transfusions from female donors with history of pregnancy. The cause of this […]
21 September 2017
Chagas disease in Europe: a review for the internist in the globalized world
Chagas Diesease or American Tripanosomiasis is a disease transmitted by Tripanosoma Cruzii, endemic in some regions of the Central and South America, discovered in 1909 by Carlos Chagas. It has only recently become a real problem in Italy when the blood donors who could have contracted the infection in some way were preventively excluded from […]
3 August 2017
Pathogen reduction/inactivation of products for the treatment of bleeding disorders: what are the processes and what should we say to patients?
Patients suffering from hematologic disorders (including leukemia, platelet disorders and coagulation factor deficiency) or from acute hemorrhagic events receive treatments based on the use of blood-derived products such as red blood cells, platelets, plasma and/or plasma-derived, Although in the last three decades the risk of serious viral infections (eg HIV, HCV, HBV) has been significantly […]
9 February 2017
An inventory of concerns behind blood safety policies in five Western countries
The availability of costly safety measures against transfusion-transmissible infections forces Western countries to confront difficult ethical questions. How to decide about implementing such measures and when are such decisions justified? As a preliminary to addressing these questions, we assessed which concerns shape actual donor blood safety policymaking in five Western countries (Canada, Germany, the Netherlands, […]
31 January 2017
Safety Issues of Plasma-Derived Products for Treatment of Inherited Bleeding Disorders
The infection by blood-borne pathogens of a large proportion of the treated hemophilia population over the 1970s to 1990s represents a major tragedy that is embedded in the history of this condition. To avoid this historical repetition, the community of patients, treaters, and policy makers that contribute to hemophilia care need to learn from the […]
31 January 2017
The current state of adverse event reporting in hemophilia
ABSTRACT Introduction: Replacement of the missing clotting factor is the mainstay of hemophilia treatment. Whilst historically many hemophilia patients were infected with blood-borne viruses transmitted via plasma-derived products, nowadays the formation of alloantibodies against the missing clotting factor is the main adverse event of treatment. Areas covered: This paper provides an overview of the current […]
21 December 2016
The risk of infection from Cytomegalovirus following transfusion
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a ubiquitous virus belonging to the herpesvirus family. The most common route of transmission is the respiratory, but it is well known that the infection can also occur through the transfusion of blood units (Transfusion Transmitted Cytomegalovirus, TTCMV). In healthy individuals the infection clinical manifestations are more often absent or very mild, […]
22 November 2016
Protocol for a national blood transfusion data warehouse from donor to recipient
Blood transfusion has health-related, economical and safety implications. In order to optimise the transfusion chain, comprehensive research data are needed. The Dutch Transfusion Data warehouse (DTD) project aims to establish a data warehouse where data from donors and transfusion recipients are linked. This paper describes the design of the data warehouse, challenges and illustrative applications. […]
10 November 2016
Viral metagenomics applied to blood donors and recipients at high risk for blood-borne infections
Background: Characterisation of human-associated viral communities is essential for epidemiological surveillance and to be able to anticipate new potential threats for blood transfusion safety. In high-resource countries, the risk of blood-borne agent transmission of well-known viruses (HBV, HCV, HIV and HTLV) is currently considered to be under control. However, other unknown or unsuspected viruses may be transmitted to recipients by blood-derived products. […]
10 November 2016
Development of blood transfusion product pathogen reduction treatments: a review of methods, current applications and demands.
Transfusion-transmitted infections (TTI) have been greatly reduced in numbers due to the strict donor selection and screening procedures, i.e. the availability of technologies to test donors for endemic infections, and routine vigilance of regulatory authorities in every step of the blood supply chain (collection, processing and storage). However, safety improvement is still a matter of concern because infection zero-risk in […]
10 October 2016
Ten-year follow-up of two cohorts with an increased risk of variant CJD: donors to individuals who later developed variant CJD and other recipients of these at-risk donors.
Abstract BACKGROUND: Transmission of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) through blood transfusion is implicated in three deaths and one asymptomatic infection. Based on this evidence, individuals assessed to be at increased risk of vCJD through donating blood transfused to individuals who later developed vCJD, or through being other recipients of such donors, are followed up to […]
30 August 2016
Hepatitis E virus infections in travellers: assessing the threat to the Australian blood supply
In developed countries hepatitis E virus (HEV) infections have occurred predominantly in travellers to countries endemic for HEV. HEV is a virus that is transmitted by blood donations. In Australia Individuals diagnosed with HEV are excluded from donating fresh blood . The aim of this study is to describe overseas-acquired HEV cases in Australia in […]
8 August 2016
A simulation model to estimate the risk of transfusion-transmitted arboviral infection
The arboviruses West Nile virus (WNV), dengue virus (DENV) and Ross River virus (RRV) are transmitted through blood. A specific statistical model for estimating the risk of WNV infection through transfusions of blood products has been developed and also applied to Chikungunya virus. Also, another probabilistic model was developed to assess the risk of DENV […]
29 February 2016
Viral metagenomics and blood safety
The characterization of the human blood-associated viral community (also called blood virome) is essential for epidemiological surveillance and to anticipate new potential threats for blood transfusion safety. Currently, the risk of blood-borne agent transmission of well-known viruses (HBV, HCV, HIV and HTLV) can be considered as under control in high-resource countries. However, other viruses unknown […]
29 February 2016
New viral risks in blood transfusion by 2016
Viral safety remains a major concern in transfusion of blood products. Over years, the control measures applied to blood products were made more and more sophisticated; however, the number of infectious agents, and notably of viruses, that can be transmitted by transfusion is increasing continuously. The aim of this review paper is to actualize that […]